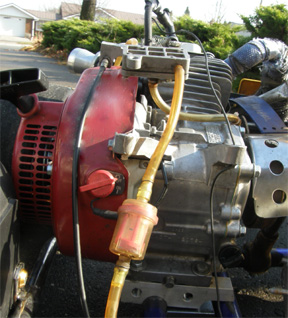
If you want to be competitive in the sport of kart racing, you’re going to need a competitive kart engine. You can spend a lot on a top of the line racing chassis, but if the engine isn't built to win, it may all be in vain. There are two "brands" of go kart engines used mainly in competitive racing which include Honda and Briggs engines. Karts used today are of different types with variety of specifications. The main component of a kart is the engine which makes it race on the track. The karts used in racing are either with 2-stroke or 4-stroke engines.
4-stroke engines can be a standard air-cooled engine which develops a power of about 5 to 20 HP. They run at around 11,000 rpm, and are manufactured specifically for karting. Briggs & Stratton and Honda are the major and widely used manufacturing brand of such engines. Yamaha, TKM, Biland or Aixro which is a wankel engine are some of the powerful four-stroke engines manufacturing brands which are not used widely but are known for the power they offer which ranges from 15 HP to 48 HP. These brands are used in some classes of two-strokes National Championships.
2-stroke kart engines are built and developed by dedicated manufacturers like WTP, Vortex, Titan, REFO, TKM, Yamaha and Rotax. Rotax is a well known engine type and there is a Rotax Max Championship which is held every year for this class of engine. 2-stroke kart engines develop power from about 8 HP for a single-cylinder 60 cc unit (MiniROK by Vortex) to 90 HP for a twin 250 cc. The most popular categories are those using the Touch-and-go (TAG) 125 cc units. The recent 125 cc KF1 engines are electronically limited at 16,000 rpm. Now-a-days water-cooled engines are used but when the sport of karting originated, air cooled engines dominated the tracks.
The Builder
If you purchase a kart engine out of a box from a dealer, chances are it will not be competitively race ready. In order to have an engine brought up to par with your competitors, you will have to find an engine builder in your area to do so. They will put your engine on a dynamometer, which will measure the torque and rotational speed (rpm) from which power produced by the engine can be calculated. The builder will then tweak the engine to produce the highest amount of torque and rpm within specifications to make your engine as fast as possible.
A 4-stroke engine can cost anywhere above INR. 20,000 and a 2-stroke engine can be above INR. 1,60,000. Well, the cost of having the engine built competitively by an engine builder can add to that cost. Overall it is a good investment for a racing engine however.
The Components
The specifics of a Honda karting engines include:
- Overhead valve single cylinder
- Spark Plugs
- Wet, multi-plate, centrifugal clutch system
- Forced air cooling system
- Forced air cooling system
- The recoil or electric start system
- Fuel tank
- Fuel tank
Upkeep
To keep your engine running efficiently from race to race, there are a few things you should do at the end of each race day before you pack away.
- Inspect your spark plug to ensure nothing has moved or been damaged during the event. For optimized engine performance, it is advisable to replace your spark plug once a year.
- Remove any used oil from the engine after race day before storing. You should change your oil generally every 20-30 minutes of track racing. This should usually last you one full race day depending on how many races you complete in a day.
- If you are going to keep the kart stationary for more than 30 days without racing, you should remove all the gasoline from the engine. Storing gasoline can cause hard starting and poor engine performance.
Keep checking our blogs for updates.
Toodles.
Chetan Vengurlekar
Toodles.
Chetan Vengurlekar